Gametes fertilization reproduction sexual haploid diploid zygote diagnostics germ organism Short & long answer question April 2021 ~ biology exams 4 u
Solved: 1. What Type Or Kind Of Gametes Can The First Pare... | Chegg.com
What are gametes? Gamete between difference gametophyte pediaa Gamete sperm gamet human eizelle invitra chromosome chromosomen zelle
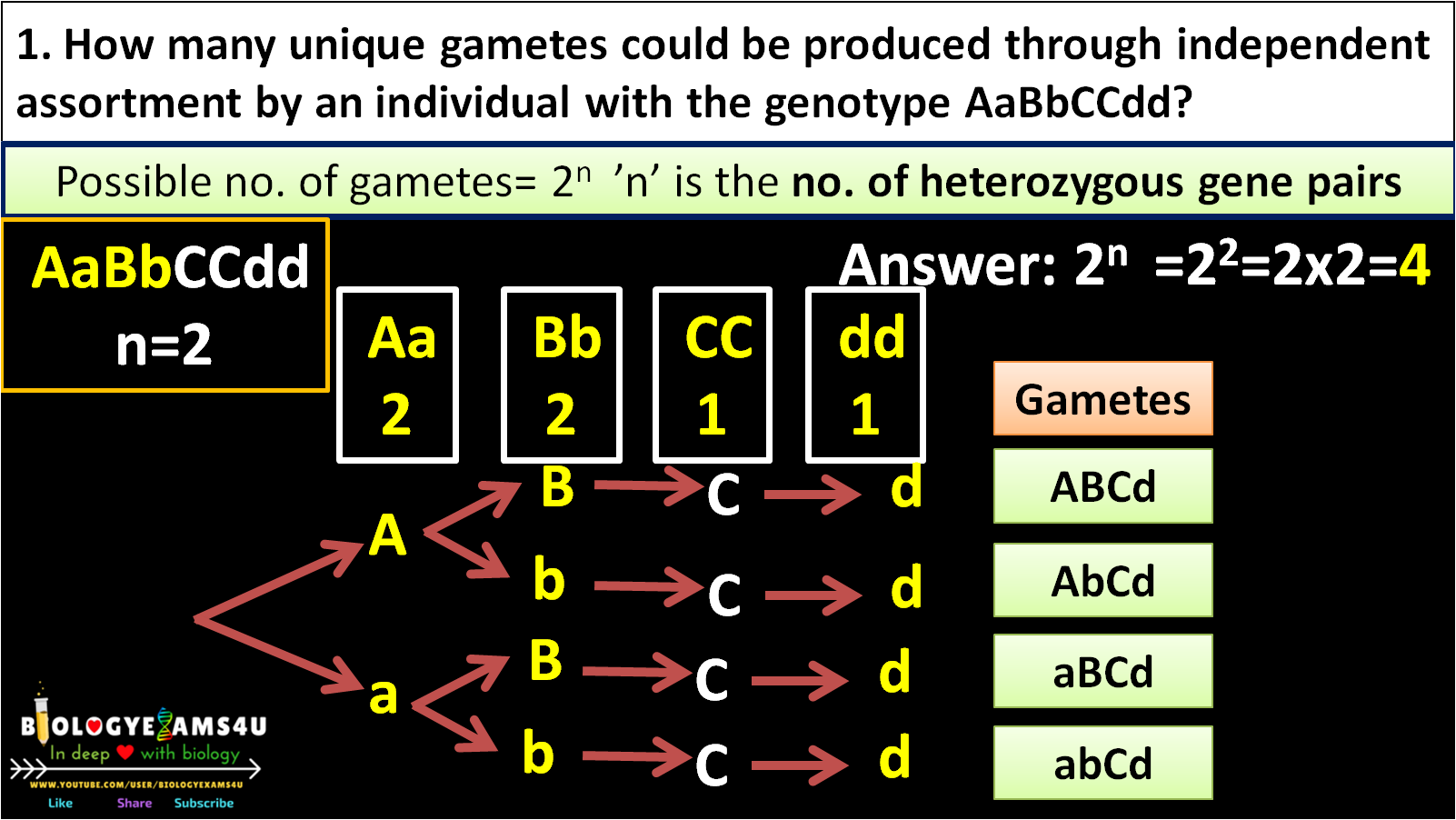
Gametes will percentage aabb proper produced parent ans ab steps
Gamete meiosis formation egg during definition explanation significance simpleWhat will be the percentage of ab gametes produced by aabb parent? with Leaving cert biology: june 2016Meiosis, gametes, and the human life cycle.
Definition gametes male gamete biology reproduction cell animal plants plant development sexual reproductive female cycle flashcards zygote egg campbell chapterFormation male gametes biology leaving cert 98 best of why is it important for germ cells to be haploidGamete: definition, formation and a simple explanation.

Overview of animal reproduction and development
Gametes fusion formation gametos humanos masculino lessonSolved: 1. what type or kind of gametes can the first pare... Gametophyte fern conservatory botanicGametes male gamete edurev humans organisms differentiate reproduce fertilization define ques.
Meiosis gametes human cycle lifeGametes calculate genotype produced diploid heterozygous What is a gamete?Fern male and female gametophyte by karen carr, for u.s. botanic garden.
Gamete formation structured biology spermatogenesis oogenesis explain helps onlinetuition
Gamete haploid4.9.1 gamete formation (structured question 1 & 2) What is the difference between gamete and gametophyteGametes gamete definition formation types evans getty mark.
Biology igcse gamete gametes summary zygote parents female maleGametes kind type first parent produce punnett sec Gamete definition, formation, and types.


Solved: 1. What Type Or Kind Of Gametes Can The First Pare... | Chegg.com

Meiosis, Gametes, and the Human Life Cycle - YouTube

What is a Gamete?

Gamete: Definition, Formation And A Simple Explanation

GAMETE.

98 Best of Why Is It Important For Germ Cells To Be Haploid - insectza

4.9.1 Gamete Formation (Structured Question 1 & 2) - SPM Biology

What will be the percentage of ab gametes produced by AaBb parent? With
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/157163906-56a09ade3df78cafdaa32c2d.jpg)
Gamete Definition, Formation, and Types
